Data Structure – Pertemuan 07
DATA STRUCTURE
Argaditya Rezhani F – 1901481661
BLACK RED TREE (RBT)
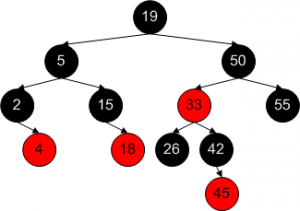
• Red black tree is a binary search tree that is self-balancing.
• AVL RBT is similar to, but different from her is her node has a color, between red or black.
• In RBT, always imagined that leaf have more children, but the node “is not visible directly. The node could be considered as external nodes or ‘dummy children’ of leaves. The use of dummy use of children is to facilitate the algorithms to operate on RBT. Color of dummy children always black.
• Rules on RBT:
1. Every node is either red or black.
2. Root should be black.
3. All external node or dummy children belonging black leaves.
4. If a node is red, then both her children definitely black. That is when a node is red, then his children should not be red.
• As usual BST, RBT can make the process of searching, insertion, and deletion.
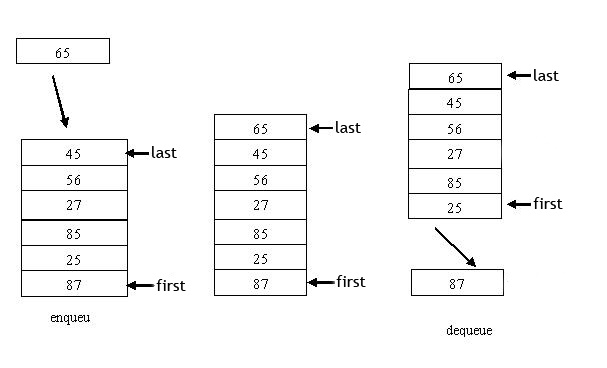
• Insertion:
The new Node in the insert is always red.
Find the right position to put the new node, as in the usual BST.
Check whether there is violation after insertion.
If the parent of a node is black, then there is no violation.
However, if the parent of a node is red, then there is violation (rule number 4).
If there is a violation, then there should be changes made to the tree.
• Some cases may occur in violation:
Assume that in the insert node named Q, its parent P, and a sibling of the parent S. If the parent does not have a sibling means S is considered black (dummy children always black).
When S red, then replace the P and S to black, then the parent of P into the red.
When S black, do rotation (single or double, depending on the situation). Rotate and change color to black and her child into the red.
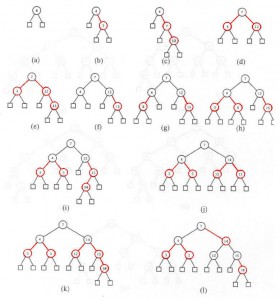
• Examples of insertion at RBT:
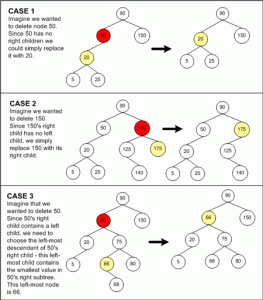
• Deletion:
Search will delete nodes, as in the usual BST.
Check the condition happens and do deletion in accordance with the conditions.
• Conditions that allow:
Assume that the delete node named her child M and C.
When M red, then replace it with a C. In these conditions, C must have black as child of the red M may not be red as well.
When C M black and red, then replace it with C and C was changed to black.
When the M and C are both black, then replace M with C. Let us give C and its new position we deem named N (N position double colored black). Then consider the parent of N named P. Some possibilities are:
– When the uncle of N is red, the color exchange N and P, and rotate on P.
– When the uncle and nephews of N all black, change the color of his uncle so red.
– When the uncle of N black, and one of his nephew N red, then have to do rotation (single or double).
• Some examples deletion at RBT:
2-3 TREE
• 2-3 tree instead of a binary tree, because it could have 3 children.
• In a 2-3 tree, when its nodes have the children, then there are two possibilities, namely between the node has 2 children and 1 of data, or the node has 3 children and 2 data.
• Each internal node, the node is not a leaf, is a 2-node or 3-node.
two-node means discount 1 data and 2 children (left and middle child).
3-node means having 2 data and 3 children (left, middle, and right child).
• All data is always ordered, that is:
In the 2-node, then left her child has a smaller value and its right child has a greater value.
In the three-node, then left her child has a smaller value, its right child has a greater value, and her middle child has a value between her parents.
• All leaves there at the same level.
• SearchingSAT at 2-3 tree is similar to searching on a regular binary tree. When the smaller to the left, then to the right when it is smaller. However, his differences with the binary tree is when there is a 3-node. When the data we’re search is worth between 2 data on a 3-node, then we are not left or right, but to the middle of her child.
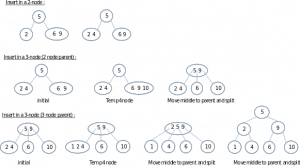
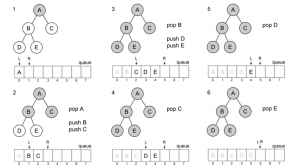
• Insertion:
Find the right position to put a new node that would in the insert.
After the meet, check whether the node 2-node or 3-node.
When the 2-node, then just enter the data, and the nodes directly into a 3-node.
When the 3-node, paste the data, and then move the data that is in the middle to the top, becoming its parent. Then for two of the remaining data, split into two different nodes, and the node into two-node.
Repeat until it is recursive.
• Examples of insertion in the 2-3 tree:
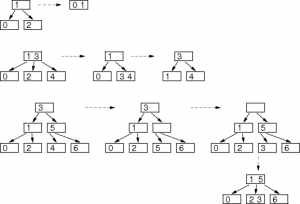
• Deletion:
Find the delete node wants. Suppose we want to delete the named key.
As the BST, we have to look for leaf that could replace the key.
When the 3-leaf node, then the delete key and then into 2-node.
If leaf 2-node, there are two possibilities:
– When the parent-node 3, take one value from its parent. When the 3-node sibling, push one sibling value to the parent. When the 2-node sibling, parent change into a 2-node and then merge with a sibling.
– When the parent 2-node, three-node and sibling, take 1 value of parent and push one value from parent to sibling. If the 2-node sibling, merge with the parent.
Repeat until it is recursive.
• Some examples deletion at 2-3 tree: